Jyh-Myng Zen 1, Jyh-Cheng Chen1 and Annamalai Senthil Kumar1 1Department of Chemistry National Chung Hsing University Taichung, Taiwan 402, R.O.C.
Received:
October 1, 2002
Accepted:
October 31, 2002
Publication Date:
December 1, 2002
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2002.5.4.03
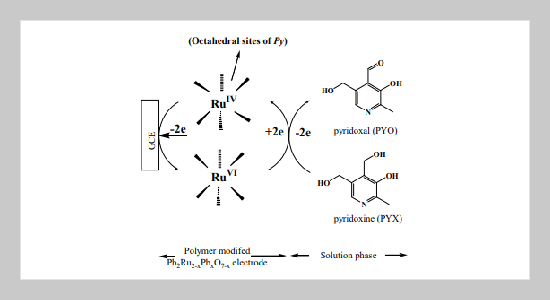
The electrocatalytic oxidation of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine hydrochloride) was demonstrated on a Nafion/lead ruthenate pyrochlore modified electrode (designated as NCME) by cyclic voltammetry. The catalytic activity of vitamin B6 was explored in terms of the higher oxidation state of ruthenium species, i.e., Py-RuIV/RuVI in the pyrochlore network (Py). The mediated mechanism was derived by Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The calculated kinetics values by direct Michaelis-Menten method are Michaelis-Menten rate constant (Km) = 4.05 mmol dm-3, catalytic rate constant (kc) = 2.05×10-1 s -1, and heterogeneous electro- chemical rate constant (k’ME) = 4.09×10-2 cm s-1.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Vitamin B6, Electrocatalysis, Chemically Modified Electrode
REFERENCES