Ching-Chang Wong This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Chi-Tai Cheng1 , Kai-Hsiang Huang1 , Yu-Ting Yang1 , Hsiang-Min Chan1 and Chii-Sheng Yin2 1Department of Electrical Engineering, Tamkang University, Tamsui, Taiwan 251, R.O.C.
2Metal Industries Research & Development Centre, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 811, R.O.C.
Received:
July 27, 2007
Accepted:
August 7, 2008
Publication Date:
September 1, 2009
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2009.12.3.04
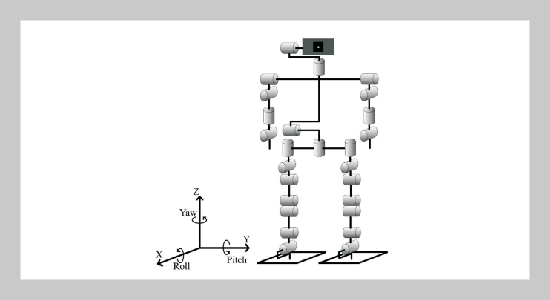
A behavior strategy of humanoid robot for obstacle avoidance based on four infrared sensors is proposed and implemented on an autonomous humanoid robot. A mechanical structure with 26 degrees of freedom is design so that an implemented small-size humanoid robot named TWNHR-III is able to accomplish five walking motions. Three walking experiments are presented to illustrate that the proposed biped structure lets TWNHR-III can move forward, turn, and slip. One electronic compass and four infrared sensors are mounted on TWNHR-III to obtain the head direction of the robot and detect obstacles, respectively. Based on the obtained information from these sensors, a decision tree method is proposed to decide one behavior from five movements: walk forward, turn right and left, and slip right and left. Two MATLAB simulations and one real experiment are presented to illustrate that the robot can avoid obstacles autonomously and go to the destination effectively.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Humanoid Robot, Autonomous Mobile Robot, Obstacle Avoidance, Decision Tree
REFERENCES