Hong Zhang1,2,3, Yijing Feng4 , Zhengxin Xiang1,2 and Ding Feng 1,2
1Hubei Engineering Research Center of Oil and Gas Drilling and Completion Tools, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei 434023, P.R. China
2Hubei Cooperative Innovation Center of Unconventional Oil and Gas, Yangtze University, Wuhan, Hubei 430100, P.R. China
3Hubei Key Laboratory of Hydroelectric Machinery Design & Maintenance, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei 443002, P.R. China
4School of Mechanical and Transportation Engineering, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, P.R. China
Received:
December 27, 2016
Accepted:
April 13, 2017
Publication Date:
December 1, 2017
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2017.20.4.04
ABSTRACT
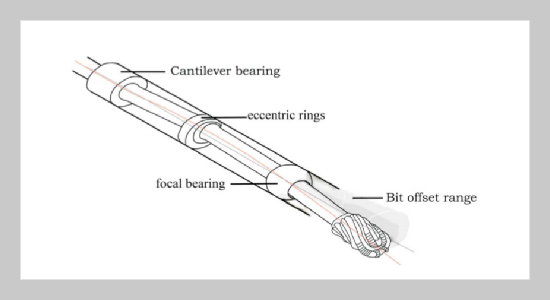
The build-up rate and steering force of the wellbore trajectory control tool has a close relationship with its shaft deformation, which mainly depends on the eccentric movement of the shaft and its flexural deformation. In combination with the working principle of the shaft of the tool, the deformation motion of the shaft was analyzed first, based on which, the flexural equation of the shaft at the static bias state was deduced as well as its angle equations, bearing reaction equations and bending moment equations. According to the deduced equations, the mechanical model of the shaft was established and optimized. To test and verify the reliability and feasibility of the model, the lab simulation experiment was carried out by using the dynamic simulation test bench of the wellbore trajectory control tool, and the bit deflection angle was acquired. A comparison was made between the data from the model and the one from the experiments. The results show that the data measured in experiments is very close to the data derived from the theoretical equations, thus verifying the feasibility of the established mechanical model of the shaft, which provides reference for the shaft design of the wellbore trajectory control tool.
Keywords:
Deformation Movement, Mechanical Model, Lab Testing, Wellbore Trajectory Control Tool, Shaft, Bias Units
REFERENCES
- [1] Downton, G., Hendrics, A., Klausen, T. S. and Pafitis, D., “New Directions in Rotary Steerable Drilling,” Oilfield Review, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 1829 (2000).
- [2] Weijermans, P., Ruszka, J., Jamshidian, H. and Matheson, M., “Drilling with Rotary Steerable System Reduces Wellbore Tortuosity,” Society of Petroleum Engineers, pp. 194203 (2013). doi: 10.2118/67715- MS
- [3] Pastusek, P., Brackin, V. J. and Lutes, P. J., “A Fundamental Model for Prediction of Hole Curvature and Build Rates with Steerable Bottomhole Assemblies,” SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, October 912 (2005). doi: 10. 2118/95546-MS
- [4] Noynaert, S. F., “AIMR (Azimuth and Inclination Modeling in Realtime): A Method for Prediction of Dogleg Severity based on Mechanical Specific Energy,” Texas A&M University (2013).
- [5] Sugiura, J., Bowler, A. and Lowdon, R., “Improved Continuous Azimuth and Inclination Measurement by Use of a Rotary-steerable System Enhances Downhole-steering Automation and Kickoff Capabilities Near Vertical,” SPE Drilling & Completion, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, September 30October 2 (2013). doi: 10.2118/166099-PA
- [6] Edwin, F., Ariel, T., Neil, D. G., Kate, M., Sivaraman, N., Richard, H., Ke, L., Stephen, J. and Fred, S., “The Best of Both Worlds-A Hybrid Rotary Steerable System,” Oilfield Review, Vol. 23, pp. 3644 (2011).
- [7] Sugiura, J., “Optimal BHA Design for Steerability and Stability with Configurable Rotary-steerable System,” SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, October 2022 (2008). doi: 10.2118/114599-MS
- [8] Iyoho, A. W., Rask, J. H., Wieseneck, J. B. and Grant, L. S., “Comprehensive Drilling Model Analyzes BHT Parameters,” SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, October 47 (2009). doi: 10.2118/124142-MS
- [9] Hobbs, G., Stinson, R., Alvord, C., Anyanwu, O. N., Klotz, C., Mohammad, M. and Huges, B., “First Field-testing of a New Rotary Steerable Drilling Liner Technology on Alaska North Slope,” IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition, Fort Worth, Texas, USA, March 46 (2014). doi: 10.2118/168044-MS
- [10] Feng, D., Wu, L., Wang, J. W., Liu, X. H., Zhang, H. and Li, H. X., “Research on Eccentric Displacement of the Trajectory Control Tool of High Build-up Rate Wellbore,” International Conference on Information Technology and Management Innovation, Guangzhou, China, November 1011 (2012).
- [11] Feng, D., Liao, Z. W., Zhang, H., Shi, L., Xia, C. Y. and Wei, S. Z., “The Study of Load Distribution for Combination Bearing in Wellbore Trajectory Control Tool,” International Conference on Electrical, Automation and Mechanical Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, July 2627 (2015). doi: 10.2991/eame-15.2015. 50
- [12] Feng, D., Xiao, A., Liao, Z. J., Xie, Y., Ruan, C. and Wang, J. W., “Loading and Axial Deformation of Finite Element Analysis of Down-hole Strings Used for Hydraulic Fracturing,” Applied Mechanics and Materials, Vol. 318, pp. 36 (2013). doi: 10.4028/www. scientific.net/AMM.318.3
- [13] Guevara, A., Sandoval, J., Guerrero, M. and Manrique, C., “Milestone in Production Using Proactive Azimuthal Deep-resistivity Sensor Combined with Advanced Geosteering Techniques: Tarapoa Block, Ecuador,” SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Mexico, April 1618 (2012). doi: 10.2118/153580-MS