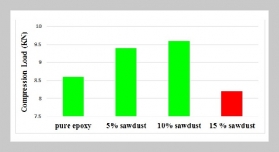
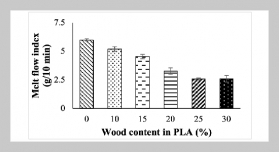
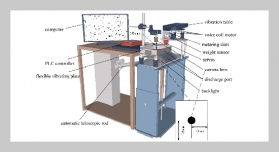
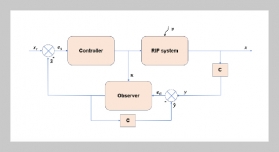
- [1] W. Chen, C. Yu, C. Tu, Z. Lyu, J. Tang, S. Ou, Y. Fu, and Z. Xue, (2020) “A survey on hand pose estimation with wearable sensors and computer-vision-based meth ods" Sensors 20(4): 1074. DOI: 10.3390/s20041074.
- [2] A.Ballester, E. Parrilla, A. Piérola, J. Uriel, C. Pérez, P. Piqueras, B. Nácher, J. A. Vivas, and S. Alemany, (2016) “Data-driven three-dimensional reconstruction of human bodies using a mobile phone app" International Journal of the Digital Human 1(4): 361–388. DOI: 10.1504/IJDH.2016.084581.
- [3] C.N.T. Kim, T. T. Vu, and B. X. Cao, (2024) “Accurate 3D reconstruction of highly reflective mechanical part surfaces using a structured light method with combined phase shift and gray code" Results in Engineering 23: 102583. DOI: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102583.
- [4] A. Kumar, D. C. Wong, H. C. Shen, and A. K. Jain, (2006) “Personal authentication using hand images" Pat tern Recognition Letters 27(13): 1478–1486. DOI: 10.1016/j.patrec.2006.02.021.
- [5] V. K. Phan, V. T. Dung, T. Van Doanh, and N. T. K. Cuc. “Apply Image Processing Techniques into the Process of Reading and Calibrating Levelling Staffs”. In: Regional Conference in Mechanical Manufacturing Engineering. Springer. 2021, 437–446. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-1968-8_35.
- [6] N.N.Kaashki,P.Hu,andA.Munteanu,(2021)“Anet: Adeep neural network for automatic 3d anthropometric measurement extraction" IEEE Transactions on Multi media 25: 831–844. DOI: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3132487.
- [7] S. Gattupalli, A. R. Babu, J. R. Brady, F. Makedon, and V. Athitsos. “Towards deep learning based hand keypoints detection for rapid sequential movements from rgb images”. In: Proceedings of the 11th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Confer ence. 2018, 31–37. DOI: 10.1145/3197768.3201538.
- [8] F. Yu, L. Zeng, D. Pan, X. Sui, and J. Tang, (2020) “Evaluating the accuracy of hand models obtained from two 3D scanning techniques" Scientific Reports 10(1): 11875. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-68457-6.
- [9] A.DERAEVE,J.COOLS,andH.BOSSAER.Theuse of 3D anthropometric data for morphotype analysis to improve fit and grading techniques. 2015. DOI: 10.15221/11.052.
- [10] A. Yu, K. L. Yick, S. Ng, and J. Yip, (2013) “2D and 3D anatomical analyses of hand dimensions for custom madegloves" Appliedergonomics44(3):381–392. DOI: 10.1016/j.apergo.2012.10.001.
- [11] A. Paoli, P. Neri, A. V. Razionale, F. Tamburrino, and S. Barone, (2020) “Sensor architectures and technolo gies for upper limb 3D surface reconstruction: a review" Sensors 20(22): 6584. DOI: 10.3390/s20226584.
- [12] A. Yu, K. Yick, S. Ng, and J. Yip, (2019) “Case study on the effects of fit and material of sports gloves on hand performance" Applied Ergonomics 75: 17–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.apergo.2018.09.007.
- [13] H. Hsiao, J. Whitestone, T.-Y. Kau, and B. Hildreth, (2015) “Firefighter hand anthropometry and structural glove sizing: a new perspective" Human factors 57(8): 1359–1377. DOI: 10.1177/0018720815594933.
- [14] M.Vergara, M.-J. Agost, and V. Bayarri, (2019) “An thropometric characterisation of palm and finger shapes to complement current glove-sizing systems" International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 74: 102836. DOI: 10.1016/j.ergon.2019.102836.
- [15] N.N.Kaashki, X. Dai, T. Gyarmathy, P. Hu, B. Iancu, and A. Munteanu. “Automatic and fast extraction of 3d hand measurements using a deep neural net work”. In: 2022 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC). IEEE. 2022, 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/I2MTC48687.2022.9806686.
- [16] A. Altaboli, H. Shamata, M. Hamed, W. Ali, H. Al shalbi, and A. Bukhatwa,(2022) “HandAnthropometry of a Sample of Libyan Young Adults from the City of Beng hazi" reason 11(16): 31.
- [17] T. Pham, P. N. Pathirana, H. Trinh, and P. Fay, (2015) “A non-contact measurement system for the range of mo tion of the hand" Sensors 15(8): 18315–18333. DOI: 10.3390/s150818315.
- [18] Q. Chen, Q.-s. Sun, P. A. Heng, and D.-s. Xia, (2008) “A double-threshold image binarization method based on edge detector" Pattern recognition 41(4): 1254–1267. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.09.007.
- [19] A. Zenner and A. Krüger. “Estimating detection thresholds for desktop-scale hand redirection in vir tual reality”. In: 2019 IEEE Conference on Virtual Re ality and 3D User Interfaces (VR). IEEE. 2019, 47–55. DOI: 10.1109/VR.2019.8798143.
- [20] T. Grzejszczak, M. Kawulok, and A. Galuszka, (2016) “Hand landmarks detection and localization in color im ages" Multimedia Tools and Applications 75: 16363 16387. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-015-2934-5.
- [21] H. S. Han and C. K. Park, (2016) “Automatic hand measurement system from 2D hand image for customized glove production" Fashion & Textile Research Journal 18(4): 468–476. DOI: 10.5805/SFTI.2016.18.4.468.
- [22] F. E. Sandnes. “A two-stage binarizing algorithm for automatic 2D: 4D finger ratio measurement of hands with non-separated fingers”. In: 2015 11th In ternational Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT). IEEE. 2015, 178–183. DOI: 10.1109/INNOVATIONS.2015.7381536.
- [23] S. Singh, N. Mittal, H. Singh, and D. Oliva, (2023) “Improving the segmentation of digital images by using a modified Otsu’s between-class variance" Multimedia Tools and Applications 82(26): 40701–40743. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-023-15129-y.
- [24] Z. Xie, J. Wu, W. Tang, and Y. Liu, (2024) “Advancing image segmentation with DBO-Otsu: Addressing rubber tree diseases through enhanced threshold techniques" Plos one 19(3): e0297284. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297284.
- [25] C.Huang, X. Li, and Y. Wen, (2021) “AN OTSU image segmentation based on fruitfly optimization algorithm" Alexandria Engineering Journal 60(1): 183–188. DOI: 10.1016/j.aej.2020.06.054.
- [26] Z. Peng, L. Wang, L. Tong, H. Zou, D. Liu, and C. Zhang, (2023) “Multi-threshold image segmentation of 2D OTSUinland ships based on improved genetic algo rithm" Plos one 18(8): e0290750. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290750.
- [27] F. Zhang, V. Bazarevsky, A. Vakunov, A. Tkachenka, G. Sung, C.-L. Chang, and M. Grundmann, (2020) “Mediapipe hands: On-device real-time hand tracking" arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.10214: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2006.10214.
- [28] F. Gu, J. Fan, Z. Wang, X. Liu, J. Yang, and Q. Zhu, (2023) “Automatic range of motion measurement via smartphone images for telemedicine examination of the hand" Science Progress 106(1): 00368504231152740. DOI: 10.1177/00368504231152740.
- [29] F. Gu, J. Fan, C. Cai, Z. Wang, X. Liu, J. Yang, and Q. Zhu, (2022) “Automatic detection of abnormal hand ges tures in patients with radial, ulnar, or median nerve injury using hand pose estimation" Frontiers in Neurology 13: 1052505. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1052505.
- [30] J. Szkudlarek, B. Zagrodny, S. Zarychta, and X. Zhao, (2023) “3D Hand Scanning Methodology for Determin ing Protective Glove Dimensional Allowances" Interna tional Journal of Environmental Research and Pub lic Health 20(3): 2645. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032645.
- [31] K. Pearson, (1893) “Contributions to the mathematical theory of evolution." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 54: 329–333.
- [32] P. J. Taylor and M. Shoben. “Grading for the Fashion Industry: The Theory and Practice”. In: 2004.
- [33] F. J. Masley, S. Lee, and A. Atkinson-Skinner. “Hand sizing tool”. US8176647B2. Filed October 8, 2010; is sued May 15, 2012. 15, 2012.
- [34] L. T. N. Anh, N. T. K. Cuc, P. T. Hien, T. T. Nga, T. VanDoanh,andT.M.Hieu.“ResearchontheCharac teristics of the Length, Breadth, and Diagonal Hand Dimensions of Male Students by Indirect Measure ment Method”. In: Advances in Asian Mechanism and Machine Science: Proceedings of IFToMM Asian MMS 2021 6. Springer. 2022, 638–648. DOI: 10.1007/978-3 030-91892-7_61.
- [35] T. Simon, H. Joo, I. Matthews, and Y. Sheikh. “Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on ComputerVisionandPattern Recognition. 2017, 1145 1153. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1704.07809.
- [36] A. Yu, K.-l. Yick, and S.-t. Wong, (2021) “Analysis of length of finger segments with different hand postures to enhance glove design" Applied Ergonomics 94: 103409. DOI: 10.1016/j.apergo.2021.103409.
- [37] N.D.Tien,N.T.K.Cuc,H.V.Van,et al. “A Design of Synergic Humanoid Robot Hand Using Finger Lock and Sensors to Achieve Adaptive Grasps”. In: 2024 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computational Cybernetics and Cyber-Medical Systems (ICCC). IEEE. 2024, 000387–000392. DOI: 10.1109/ICCC62278.2024.10582967.