Yung-Chiang Ting1 , Fuh-Gue Chen2 , Yu-Ju Ku2 , Raymond Lin2 and Chung K. Lai This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.2 1Department of Chemical Engineering Far East Technology College Shinshr, Taiwan 744, R.O.C.
2Department of Chemistry National Central University Chungli, Taiwan 320, R.O.C.
Received:
July 30, 2002
Accepted:
August 29, 2002
Publication Date:
September 1, 2002
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2002.5.3.08
{xpdfattach}
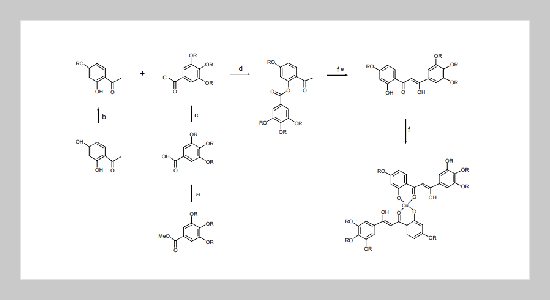
Two homologous series of mono-copper(II) complexes (1a - 1b) derived from β,δ-triketones; 1-(2’-hydroxy-4’-alkoxyphenyl)-3-(3’, 4’,5’-trialkoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diones and 1-(2’-hydroxyphenyl)- 3-(3’,4’,5’-trialkoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diones were prepared and their mesomorphic properties studied. These green copper(II) complexes were prepared by the reaction of β,δ-triketones with half equivalent of copper(II) acetate in the presence of KOH. The complexes were characterized by 1 H NMR, 13C NMR, IR spectroscopy and elemental analysis, and the liquid crystalline behavior of these complexes was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and optical polarized microscope. The mesophase was identified as disordered hexagonal columnar mesophases (Colh) based on optical textures observed. The compounds 1b showed a higher clearing temperature and a wider range of phase temperature than those of compounds 1a, and the difference in mesomorphic temperatures might be mainly attributed from a better dipolar interaction from the extra alkoxyl groups by compounds 1b.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Metallomesogenic Materials, Liquid Crystal, Copper(II) Complexes, Synthesis.
REFERENCES