Department of Architectural Engineering, Shijiazhuang College of Applied Technology, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
Received:
February 18, 2024
Accepted:
September 12, 2024
Publication Date:
November 16, 2024
Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are cited.
Download Citation: ||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.202508_28(8).0012
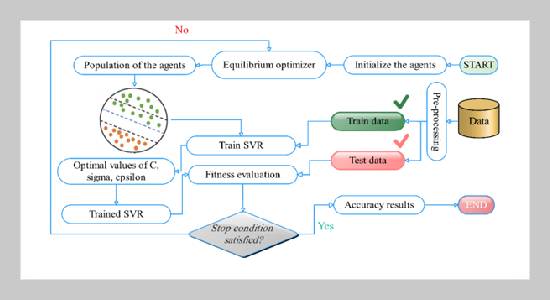
Different regression analytics were used to provide a unique approach to testing the compressive strength (CS) of high-performance concrete (HPC) made with blast furnace slag and fly ash. In this study, it was employed the equilibrium optimizer (EO) and the arithmetic optimization algorithm (AOA) to identify key regression method variables (i.e., Support vector regression (SVR)) which could be adjusted to improve performance. The suggested approaches were created utilizing 1030 tests, eight inputs (aggregates, primary mix designs, admixtures, and curing age), and the CS as the forecasting objective. The results were then compared to those in the corpus of already published scientific literature. Estimation outcomes point to the potential benefit of combining EO-SVR with AOA-SVR analysis. The AOA-SVR displayed significantly better R2 (0.9874 and 0.993) and lower RMSEvalues as compared to the EO-SVR. Comparing the data demonstrates how much better the created AOA-SVR is than anything that has previously been reported. Overall, the suggested technique for determining the CS of HPC augmented with fly ash and blast furnace slag may be used using the AOA-SVR analysis.
Keywords:
Compressive Strength; Blast Furnace Slag; High-Performance Concrete; Support Vector Regression; Fly Ash; Artificial Intelligence
- [1] I.-C. Yeh, (2007) “Modeling slump flow of concrete using second-order regressions and artificial neural networks" Cement andconcrete composites 29: 474–480. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2007.02.001.
- [2] T. Ji, T. Lin, and X. Lin, (2006) “A concrete mix propor tion design algorithm based on artificial neural networks" Cement and Concrete Research 36: 1399–1408. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.01.009.
- [3] M.Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “En semble extreme gradient boosting based models to predict the bearing capacity of micropile group" Applied Ocean Research 151: 104149. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2024.104149.
- [4] R. S. Benemaran, (2023) “Application of extreme gra dient boosting method for evaluating the properties of episodic failure of borehole breakout" Geoenergy Sci ence and Engineering 226: 211837. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211837.
- [5] A.A.Basma, S. A. Barakat, and S. Al-Oraimi, (1999) “Prediction of cement degree of hydration using artificial neural networks" ACI Materials Journal 96: 167–172. DOI: 10.14359/441.
- [6] M.Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “Ap plication of optimization-based regression analysis for eval uation of frost durability of recycled aggregate concrete" Structural Concrete 25: 716–737. DOI: 10.1002/suco. 202300566.
- [7] I.-C. Yeh, (1998) “Modeling of strength of high performance concrete using artificial neural networks" Cement and Concrete research 28: 1797–1808. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00165-3.
- [8] P. L. J. Domone and M. N. Soutsos, (1994) “Approach to the proportioning of high-strength concrete mixes" Concrete international 16: 26–31.
- [9] S. M. Mousavi, A. H. Gandomi, A. H. Alavi, and M. Vesalimahmood, (2010) “Modeling of compressive strength of HPC mixes using a combined algorithm of ge netic programming and orthogonal least squares" Struc tural Engineering and Mechanics, An Int’l Journal 36: 225–241. DOI: 10.12989/sem.2010.36.2.225.
- [10] R. A. Cook, C. Goodspeed, and S. Vanicar. High performance concrete defined for highway structures. 1998.
- [11] A. M.Andrew, (2001) “An introduction to support vec tor machines and other kernel-based learning methods" Kybernetes 30: 103–115. DOI: 10.1108/k.2001.30.1.103.6.
- [12] A. J. Smola and B. Schölkopf, (2004) “A tutorial on support vector regression" Statistics and computing 14: 199–222. DOI: 10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88.
- [13] L.Abualigah,A.Diabat,S.Mirjalili, M. A. Elaziz, and A. H. Gandomi, (2021) “The arithmetic optimization algorithm" Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 376: 113609. DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113609.
- [14] A. Faramarzi, M. Heidarinejad, B. Stephens, and S. Mirjalili, (2020) “Equilibrium optimizer: A novel opti mization algorithm" Knowledge-based systems 191: 105190. DOI: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105190.
- [15] J. Benesty, J. Chen, Y. Huang, and I. Cohen. Noise reduction in speech processing. 2. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-00296-0.
- [16] M.S.KhorsheedandA.O.Al-Thubaity, (2013) “Com parative evaluation of text classification techniques using a large diverse Arabic dataset" Language resources and evaluation 47: 513–538. DOI: 10.1007/s10579-013-9221-8.
- [17] N. Leema, H. K. Nehemiah, and A. Kannan, (2016) “Neural network classifier optimization using differential evolution with global information and back propagation al gorithm for clinical datasets" Applied Soft Computing 49: 834–844. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.08.001.
- [18] I.-C. Yeh, (1998) “Modeling concrete strength with augment-neuron networks" Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 10: 263–268. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(1998)10:4(263).
- [19] I.-C. Yeh, (2006) “Analysis of strength of concrete using design of experiments and neural networks" Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 18: 597–604. DOI: 10. 1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2006)18:4(597).
- [20] I.-C. Yeh, (2003) “Prediction of strength of fly ash and slag concrete by the use of artificial neural networks" J. Chin. Inst. Civil Hydraul. Eng 15: 659–663.
- [21] I.-C. Yeh, (1999) “Design of high-performance concrete mixture using neural networks and nonlinear program ming" Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 13: 36–42. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(1999)13: 1(36).
- [22] S. Lee, N.-H. Nguyen, A. Karamanli, J. Lee, and T. P. Vo, (2023) “Super learner machine-learning algorithms for compressive strength prediction of high performance concrete" Structural Concrete 24: 2208–2228. DOI: 10.1002/suco.202200424.
- [23] D. V. Dao, H. Adeli, H.-B. Ly, L. M. Le, V. M. Le, T.-T. Le, and B. T. Pham, (2020) “A sensitivity and ro bustness analysis of GPR and ANN for high-performance concrete compressive strength prediction using a Monte Carlo simulation" Sustainability 12: 830. DOI: 10.3390/ su12030830.
- [24] N.-H. Nguyen, T. P. Vo, S. Lee, and P. G. Asteris, (2021) “Heuristic algorithm-based semi-empirical formu las for estimating the compressive strength of the nor mal and high performance concrete" Construction and Building Materials 304: 124467. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124467.
- [25] P. G. Asteris, A. D. Skentou, A. Bardhan, P. Samui, and K. Pilakoutas, (2021) “Predicting concrete com pressive strength using hybrid ensembling of surrogate machine learning models" Cement and Concrete Re search 145: 106449. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106449.
- [26] S. M. Mousavi, P. Aminian, A. H. Gandomi, A. H. Alavi, and H. Bolandi, (2012) “A new predictive model for compressive strength of HPC using gene expression programming" Advances in Engineering Software 45: 105–114. DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.09.014.
- [27] A. H.GandomiandA.H.Alavi, (2012) “A new multi gene genetic programming approach to nonlinear system modeling. Part I: materials and structural engineering problems" Neural Computing and Applications 21: 171–187. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-011-0734-z.
- [28] A. H.GandomiandA.H.Alavi, (2012) “A new multi gene genetic programming approach to non-linear system modeling. Part II: geotechnical and earthquake engineer ing problems" Neural Computing and Applications 21: 189–201. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-011-0735-y.
- [29] J. Koza, (1992) “On the programming of computers by meansof natural selection" Genetic programming: DOI: 978-0-262-11170-6.
- [30] M.H.Rafiei, W.H.Khushefati, R. Demirboga, and H. Adeli, (2017) “Supervised deep restricted Boltzmann ma chine for estimation of concrete" ACI Materials Journal 114: 237. DOI: 10.14359/51689560.
- [31] P. G.Asteris, P. C. Roussis, and M. G. Douvika, (2017) “Feed-forward neural network prediction of the mechanical properties of sandcrete materials" Sensors 17: 1344. DOI: 10.3390/s17061344.
- [32] M.R. Kaloop, D. Kumar, P. Samui, J. W. Hu, and D. Kim, (2020) “Compressive strength prediction of high performance concrete using gradient tree boosting ma chine" Construction and Building Materials 264: 120198. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120198.
- [33] H. I. Erdal, (2013) “Two-level and hybrid ensembles of decision trees for high performance concrete compressive strength prediction" Engineering Applications of Ar tificial Intelligence 26: 1689–1697. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2013.03.014.
- [34] M.-Y. Cheng, P. M. Firdausi, and D. Prayogo, (2014) “High-performance concrete compressive strength predic tion using Genetic Weighted Pyramid Operation Tree (GWPOT)" Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 29: 104–113. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai. 2013.11.014.
- [35] J.-S. Chou and A.-D. Pham, (2013) “Enhanced artificial intelligence for ensemble approach to predicting high per formance concrete compressive strength" Construction and Building Materials 49: 554–563. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.08.078.
- [36] H.I. Erdal, O. Karakurt, and E. Namli, (2013) “High performance concrete compressive strength forecasting us ing ensemble models based on discrete wavelet transform" Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 26: 1246–1254. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2012.10.014.
- [37] S. Rajasekaran and S. Lavanya, (2007) “Hybridization of genetic algorithm with immune system for optimiza tion problems in structural engineering" Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 34: 415–429. DOI: 10.1007/s00158-006-0084-0.
- [38] S. Rajasekaran, D. Suresh, and G. A. V. Pai, (2002) “Application of sequential learning neural networks to civil engineering modeling problems" Engineering with Computers 18: 138–147. DOI: 10.1007/s003660200012.
- [39] B. K. R. Prasad, H. Eskandari, and B. V. V. Reddy, (2009) “Prediction of compressive strength of SCC and HPCwith high volume fly ash using ANN" Construc tion and Building Materials 23: 117–128. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.01.014.
- [40] S. Rajasekaran and R. Amalraj, (2002) “Predictions of design parameters in civil engineering problems using SLNN with a single hidden RBF neuron" Computers & structures 80: 2495–2505. DOI: 10.1016/S0045 7949(02)00213-4.
- [41] J. Kasperkiewicz, J. Racz, and A. Dubrawski, (1995) “HPC strength prediction using artificial neural network" Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 9: 279 284. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(1995)9:4(279).
- [42] B. Sadaghat, S. A. Ebrahimi, O. Souri, M. Y. Niar, and M. R. Akbarzadeh, (2024) “Evaluating strength properties of Eco-friendly Seashell-Containing Concrete: Comparative analysis of hybrid and ensemble boosting methods based on environmental effects of seashell usage" Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 133: 108388. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108388.